Table | Charts | Pseudocode
Introduction:
This page details the strict filtering happening on the SIX route servers.
When a prefix is advertised, the route server performs a series of tests to decide whether the prefix may be accepted. If a prefix fails to pass any test, it is dropped prior to further tests. One could imagine that a prefix has to "run the gauntlet" before it may be accepted and propagated to route server peers. For each route server instance, the table below lists these tests in the order they occur. The counts in the table reflect the number of unique drops for a test since the start of the UTC day. Clicking a count reveals further details.
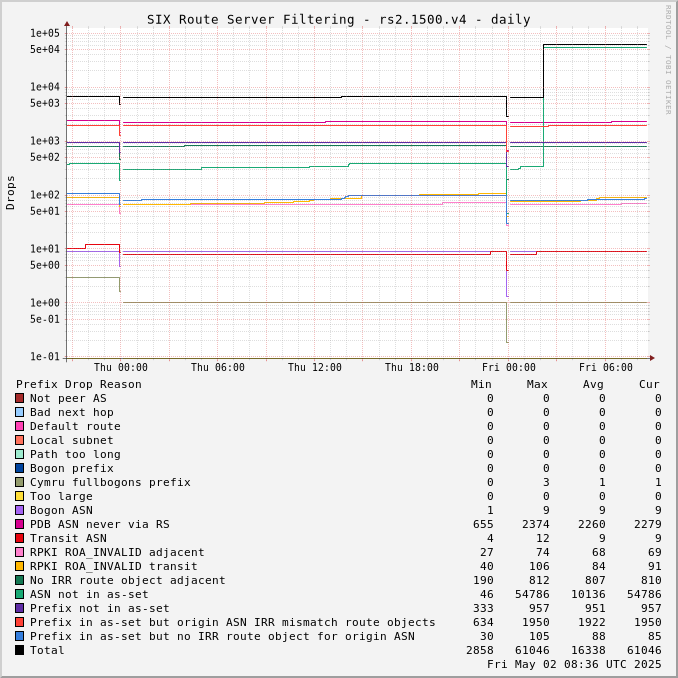
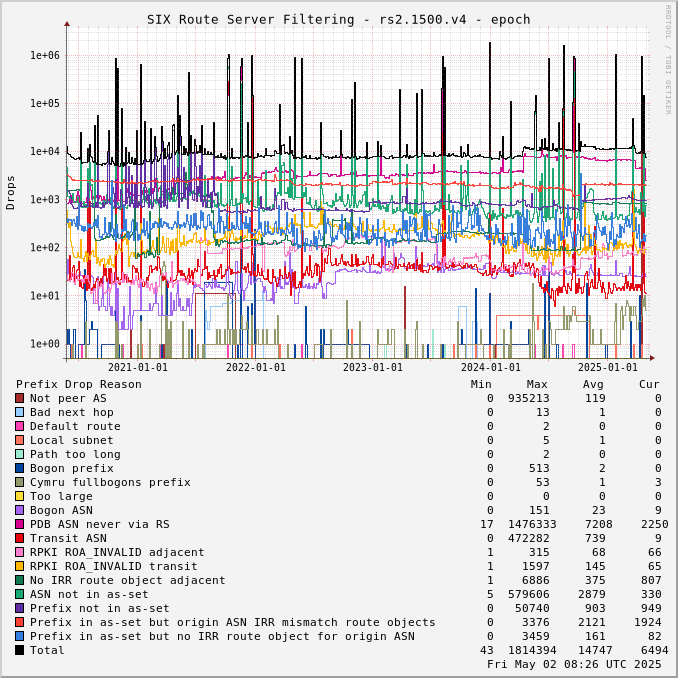
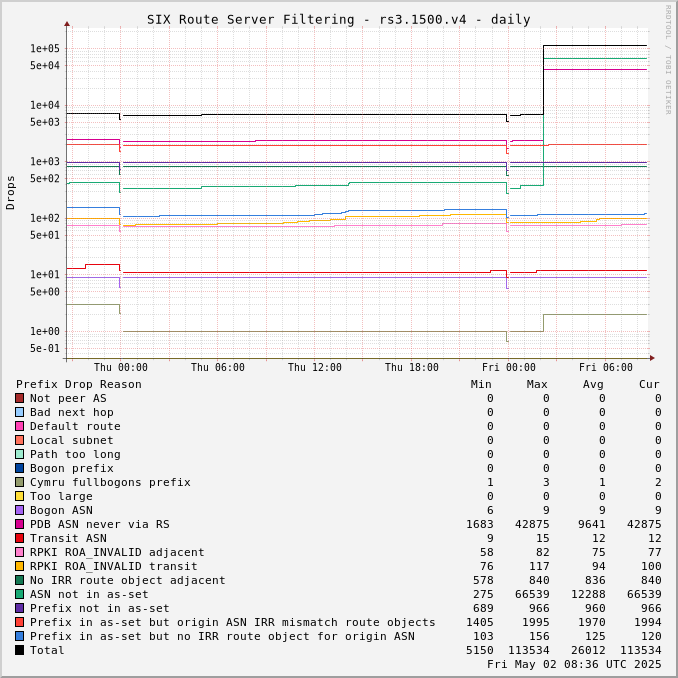
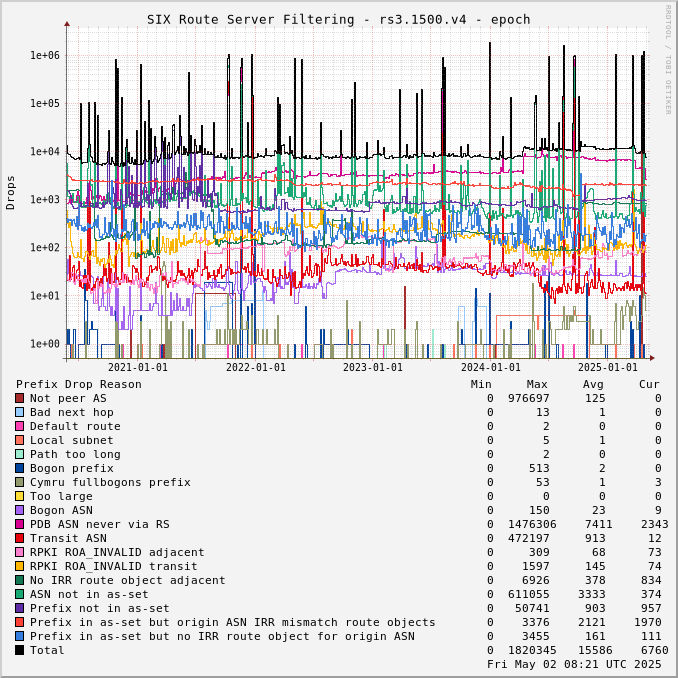
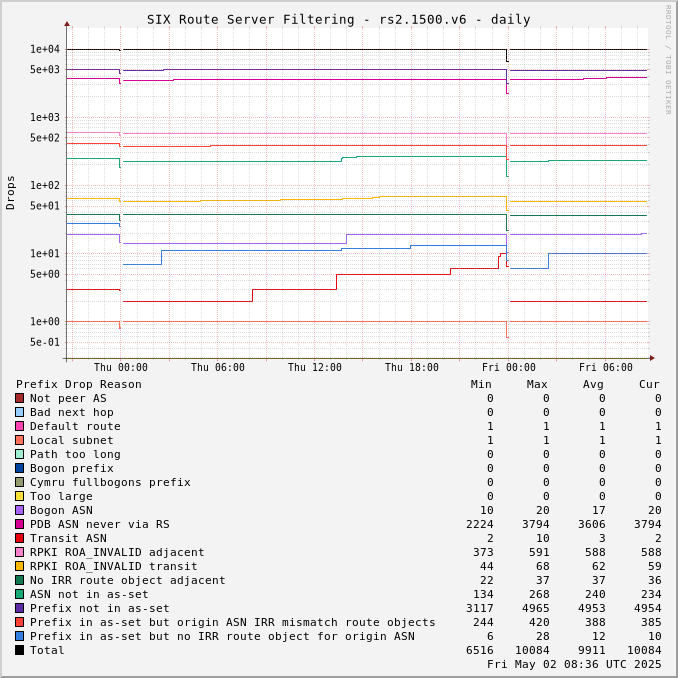
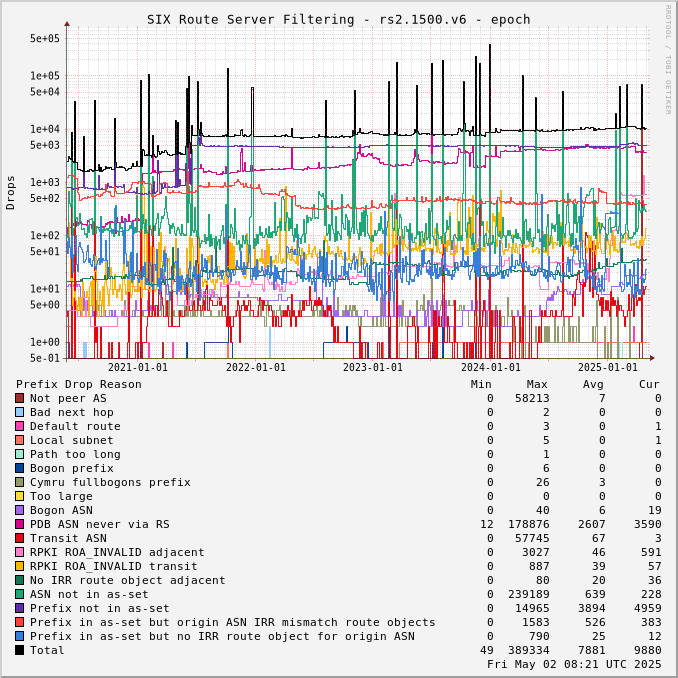
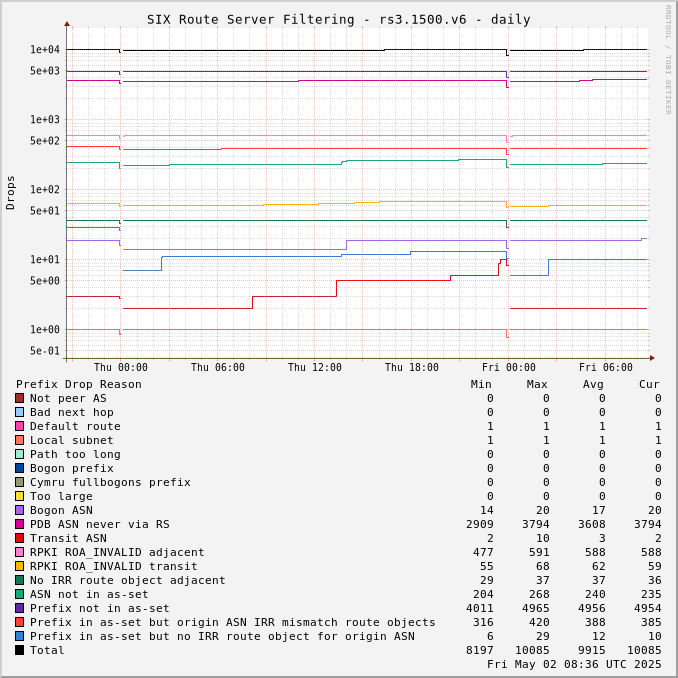
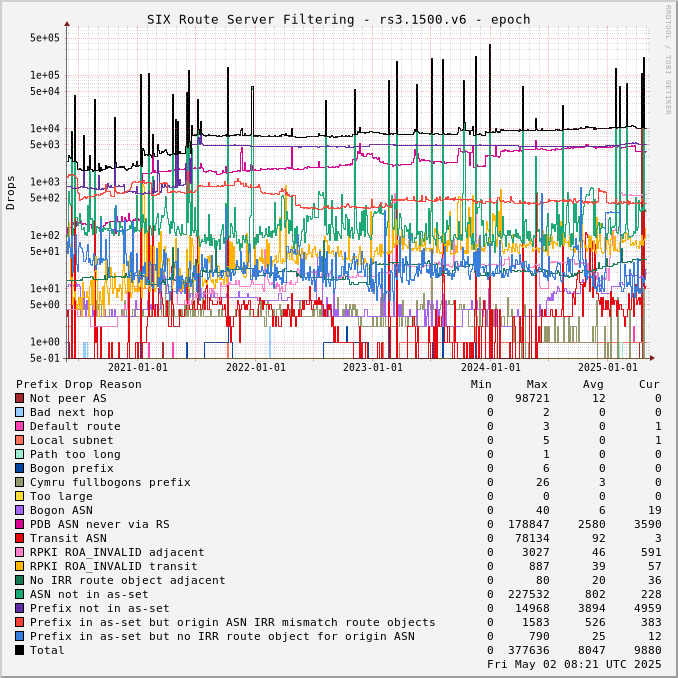
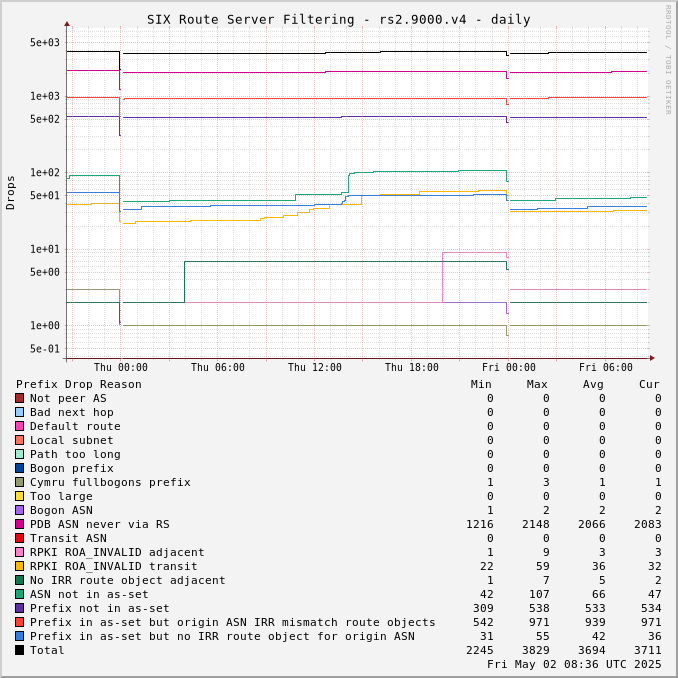
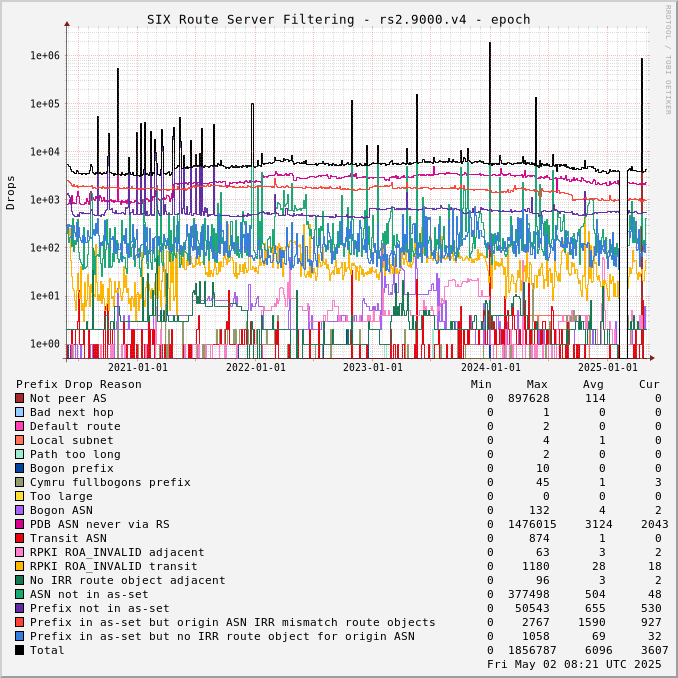
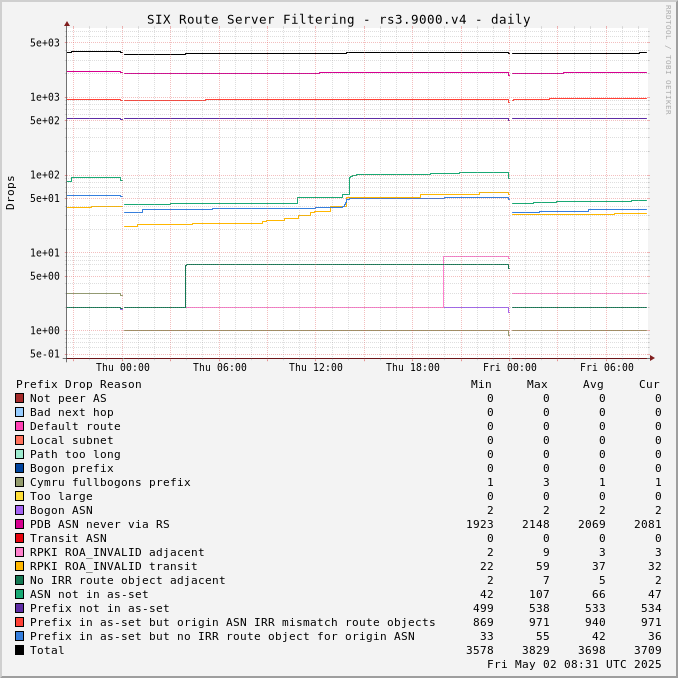
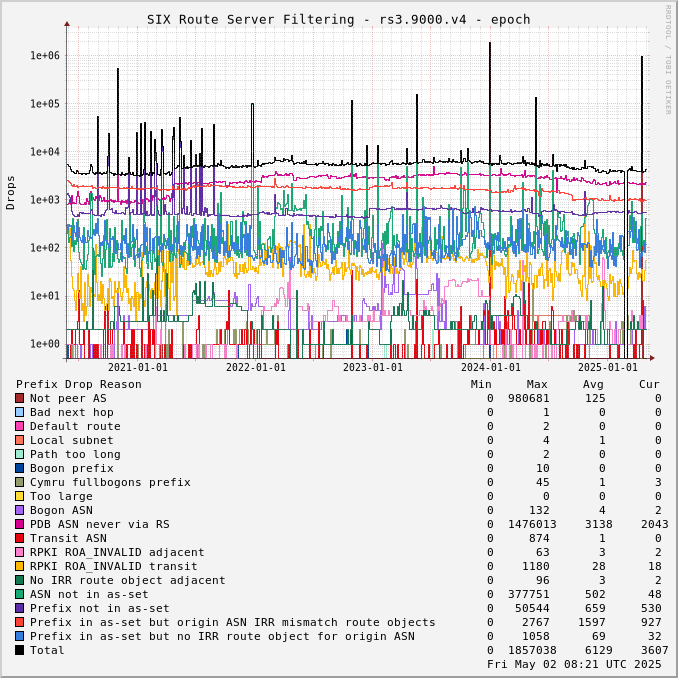
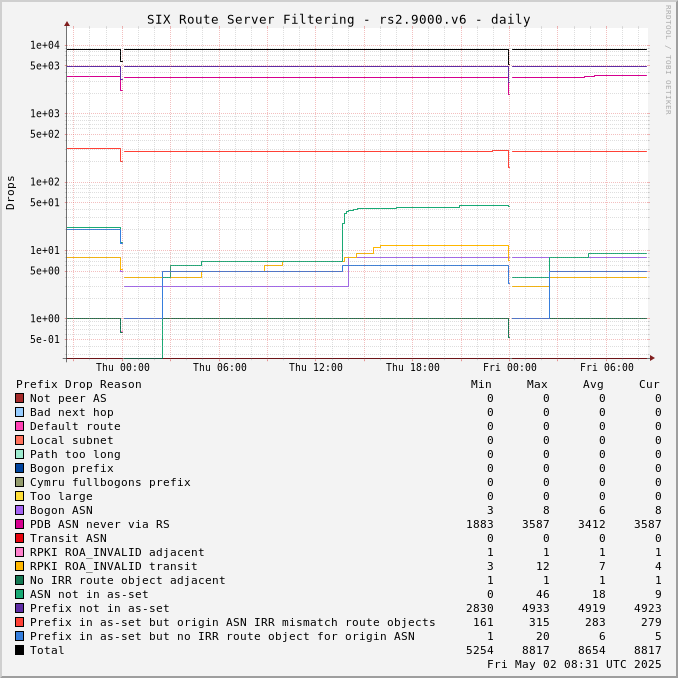
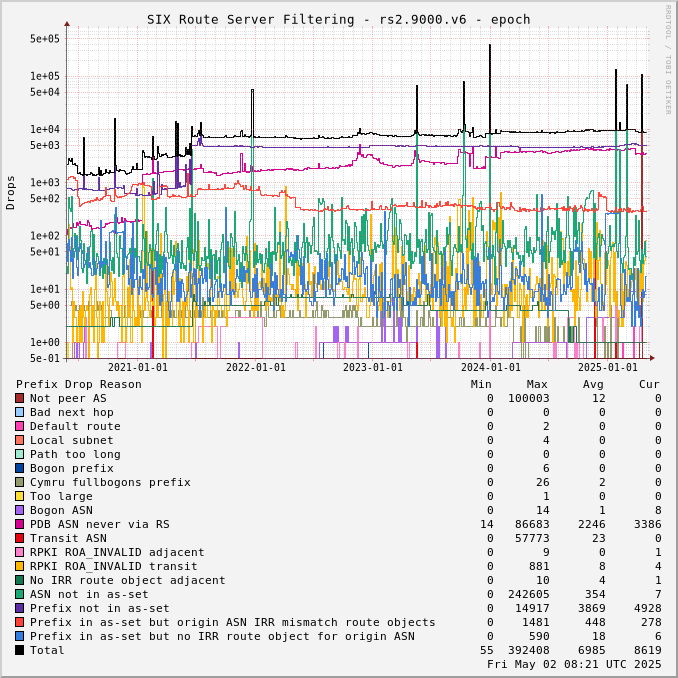
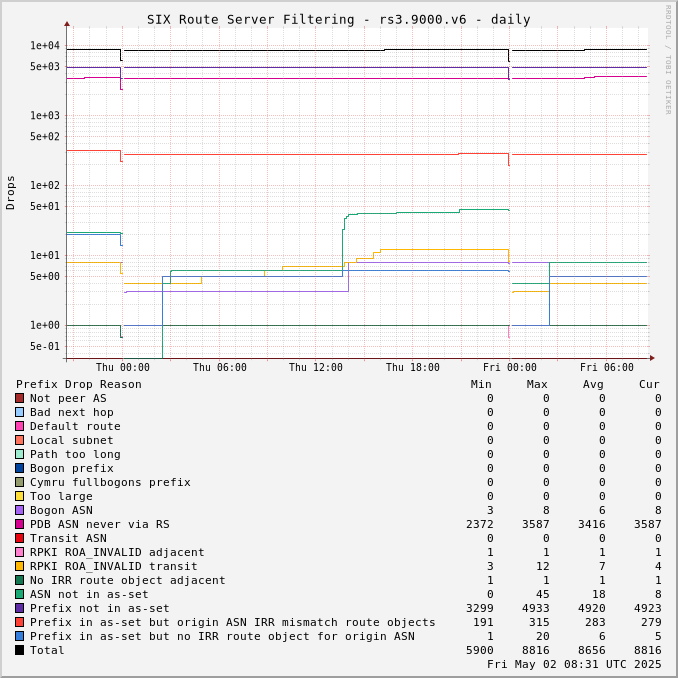
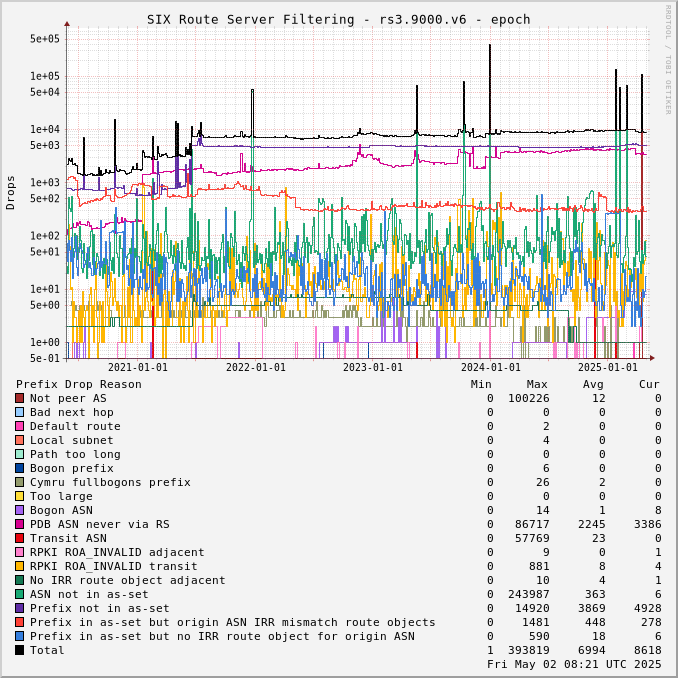
The charts below show drops over time, enabling the perception of network events and adoption of industry standards like RPKI.
Drops for a specific ASN can be viewed by adjusting the URL for this page to include "?asn=#" with "#" changed to the ASN of interest.
Pseudocode showing how the SIX performs filtering is also below.
Feel free to email info_a_t_seattleix.net with any bug fixes to the pseudocode or other feedback about this page.
Route server drops since start of UTC day:
Prefix Drop Reason (in order of tests) | rs2.1500.v4 | rs3.1500.v4 | rs2.1500.v6 | rs3.1500.v6 | rs2.9000.v4 | rs3.9000.v4 | rs2.9000.v6 | rs3.9000.v6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Not peer AS | ||||||||
Bad next hop | ||||||||
Default route | ||||||||
Local subnet | ||||||||
Path too long | ||||||||
Bogon prefix | ||||||||
Cymru fullbogons prefix | ||||||||
Too large | ||||||||
Bogon ASN | ||||||||
PeeringDB ASN never via RS | ||||||||
Transit ASN | ||||||||
RPKI ROA_INVALID adjacent | ||||||||
RPKI ROA_INVALID transit | ||||||||
No IRR route object adjacent | ||||||||
ASN not in as-set | ||||||||
Prefix not in as-set | ||||||||
Prefix in as-set but origin ASN IRR mismatch route objects | ||||||||
Prefix in as-set but no IRR route object for origin ASN | ||||||||
Total |
BIRD filter pseudo-code:
#if IPv4
# http://bgpfilterguide.nlnog.net/guides/bogon_prefixes/
define BOGON_PREFIXES = [ 0.0.0.0/8+, # RFC 1122 'this' network
10.0.0.0/8+, # RFC 1918 private space
100.64.0.0/10+, # RFC 6598 Carrier grade nat space
127.0.0.0/8+, # RFC 1122 localhost
169.254.0.0/16+, # RFC 3927 link local
172.16.0.0/12+, # RFC 1918 private space
192.0.2.0/24+, # RFC 5737 TEST-NET-1
192.88.99.0/24+, # RFC 7526 6to4 anycast relay
192.168.0.0/16+, # RFC 1918 private space
198.18.0.0/15+, # RFC 2544 benchmarking
198.51.100.0/24+, # RFC 5737 TEST-NET-2
203.0.113.0/24+, # RFC 5737 TEST-NET-3
224.0.0.0/4+, # multicast
240.0.0.0/4+ ]; # reserved
#else
# http://www.space.net/~gert/RIPE/ipv6-filters.html
# http://bgpfilterguide.nlnog.net/guides/bogon_prefixes/
define BOGON_PREFIXES = [ ::/8+, # RFC 4291 IPv4-compatible, loopback, et al
0100::/64+, # RFC 6666 Discard-Only
2001:2::/48+, # RFC 5180 BMWG
2001:10::/28+, # RFC 4843 ORCHID
2001:db8::/32+, # RFC 3849 documentation
2002::/16+, # RFC 7526 6to4 anycast relay
3ffe::/16+, # RFC 3701 old 6bone
fc00::/7+, # RFC 4193 unique local unicast
fe80::/10+, # RFC 4291 link local unicast
fec0::/10+, # RFC 3879 old site local unicast
ff00::/8+ ]; # RFC 4291 multicast
#endif
# http://as2914.net/bogon_asns/configuration_examples.txt
# http://bgpfilterguide.nlnog.net/guides/bogon_asns/
define BOGON_ASNS = [ 0, # RFC 7607
23456, # RFC 4893 AS_TRANS
64496..64511, # RFC 5398 and documentation/example ASNs
64512..65534, # RFC 6996 Private ASNs
65535, # RFC 7300 Last 16 bit ASN
65536..65551, # RFC 5398 and documentation/example ASNs
65552..131071, # IANA reserved ASNs https://www.mail-archive.com/uknof@lists.uknof.org.uk/msg03395.html
4200000000..4294967294, # RFC 6996 Private ASNs
4294967295 ]; # RFC 7300 Last 32 bit ASN
# http://bgpfilterguide.nlnog.net/guides/no_transit_leaks/
define TRANSIT_ASNS = [ 174, # Cogent
209, # Qwest (HE carries this on IXPs IPv6 (Jul 12 2018))
701, # UUNET
702, # UUNET
1239, # Sprint
1299, # Telia
2914, # NTT Communications
3257, # GTT Backbone
3320, # Deutsche Telekom AG (DTAG)
3356, # Level3
3491, # PCCW
3549, # Level3
3561, # Savvis / CenturyLink
4134, # Chinanet
5511, # Orange opentransit
6453, # Tata Communications
6461, # Zayo Bandwidth
6762, # Seabone / Telecom Italia
6830, # Liberty Global
7018 ]; # AT&T
function net_local()
{
#if IPv4
return net ~ [ 149.112.96.0/22+, 206.81.80.0/22+ ]; # matches all subprefixes of SIX address spaces 149.112.96.0/22 and 206.81.80.0/22
#else
return net ~ [ 2001:504:16::/48+ ]; # matches all sub-prefixes of SIX address space 2001:504:16::/48
#endif
}
function next_hop_local()
{
#if IPv4
return bgp_next_hop ~ 206.81.80.0/22; # matches SIX address space 206.81.80.0/22
# or
return bgp_next_hop ~ 149.112.96.0/22; # matches SIX address space 149.112.96.0/22
#else
return bgp_next_hop ~ 2001:504:16::/48; # matches SIX address space 2001:504:16::/48
#endif
}
function rt_import(int peeras; prefix set peer_nets; int set peer_asns; prefix set as_set_nets)
int path_max;
int rpki_roa_valid;
{
if bgp_path.first != peeras then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": bgp_path.first(", bgp_path.first, ") != peeras(", peeras, ")! Dropping.";
return false;
}
if ! next_hop_local() then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": bgp_next_hop(", bgp_next_hop, ") not local! Dropping.";
return false;
}
#if IPv4
# Avoid 0.0.0.0/X
if net.ip = 0.0.0.0 then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": net.ip = 0.0.0.0! Dropping.";
return false;
}
#else
# Avoid ::/X
if net.ip = :: then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": net.ip = ::! Dropping.";
return false;
}
#endif
if net_local() then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": net_local() returned true! Dropping.";
return false;
}
path_max = 128;
if bgp_path.len > path_max then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": bgp_path.len(", bgp_path.len, ") > ", path_max, "! Dropping.";
return false; # limit AS_PATH length (to prevent problems with misconfigured routers
# propagating too long path and buggy routers crashing on that)
}
if net ~ BOGON_PREFIXES then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": matches bogon_prefixes! Dropping.";
return false;
}
if net ~ CYMRU_FULLBOGONS_PREFIXES then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": matches cymru_fullbogons_prefixes! Dropping.";
return false;
}
#if IPv4
if net.len < 8 then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": net.len < 8! Dropping.";
return false;
}
#else
if net.len < 19 then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": net.len < 19! Dropping.";
return false;
}
#endif
if bgp_path ~ BOGON_ASNS then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": matches bogon_ASNs! Dropping.";
return false;
}
if bgp_path ~ PDB_NEVER_VIA_ROUTE_SERVERS_ASNS then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": matches pdb_never_via_route_servers_ASNs! Dropping.";
return false;
}
if bgp_path ~ TRANSIT_ASNS then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": matches transit_ASNs! Dropping.";
return false;
}
rpki_roa_valid = 0;
case roa_check(ROAS, net, bgp_path.last_nonaggregated)
{
ROA_INVALID:
if bgp_path.last_nonaggregated = peeras then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": RPKI ROA_INVALID! Dropping.";
} else {
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": RPKI ROA_INVALID! Transit_dropping.";
}
return false;
ROA_VALID:
rpki_roa_valid = 1;
}
if bgp_path.last_nonaggregated = peeras then
{
# IRR route object verification is not needed when RPKI ROA is valid.
if 0 = rpki_roa_valid then
{
# Route is from peer ASN, so just check peer prefix list.
if ! (net ~ peer_nets) then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": no IRR route object found! Dropping.";
return false;
}
}
} else {
# Route is not from peer ASN, so check peer ASN list.
if ! (bgp_path.last_nonaggregated ~ peer_asns) then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": AS", bgp_path.last_nonaggregated, " not member of IRR as-set object! Dropping.";
return false;
}
# IRR route object verification is not needed when RPKI ROA is valid.
if 0 = rpki_roa_valid then
{
# Route is not from peer ASN, so check peer as-set prefix list.
if ! (net ~ as_set_nets) then
{
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": no IRR route object with matching origin found! Transit_dropping.";
return false;
}
# The IRR-based ROAs table we use here must include all prefixes, both from
# adjacent ASN and downstream ASNs.
#
# ROA_VALID: if there is a matching ROA
# ROA_INVALID: if there are some relevant ROAs but none of them match
# ROA_UNKNOWN: if there is no relevant ROA
#
# We test for ROA_INVALID and ROA_UNKNOWN here, and return false if either happens,
# because to get here means the following:
#
# - this prefix is from a non-adjacent ASN
# - the last ASN is in the as-set
# - the prefix is in the as-set
#
# so what we are testing here is to make sure the prefix has the correct AS origin.
# A return of ROA_INVALID or ROA_UNKNOWN means it does not.
#
# ROA_UNKNOWN can happen if the IRR as-set prefix list includes a covering prefix,
# but none of the perceived ASNs has an IRR entry for the prefix.
#
case roa_check(IRR, net, bgp_path.last_nonaggregated)
{
ROA_INVALID:
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": no IRR route object with matching origin found (ROA_INVALID)! Transit_dropping.";
return false;
ROA_UNKNOWN:
print proto, ": ", net, " from ", from, " ", bgp_path, ": no IRR route object with matching origin found (ROA_UNKNOWN)! Transit_dropping.";
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}